Optimized division of uint64_t by a constant on 32-bit microcontrollers
Written 2022-07-21
Tags:Optimization Multiplication ARM Division
Problem Statement
Recently, I ran into a bottleneck and my profiler highlighted that a large fraction of program time was being spent in __aeabi_uldivmod(), an ARM math support function for division with the following prototype:
struct result {
u64 quot, rem;
};
struct result __aeabi_uldivmod(u64 numerator, u64 denominator)
{
struct result res;
//compute res here
return res;
}
There's several differeny ways to implement __aeabi_uldivmod(), including 1-bit-at-a-time long division, the same with speedup from a count-leading-zeros instrucion like ARM's CLZ, or 32-bit-at-a-time long-division using the udiv instruction present on some ARM cores.
A partial solution
But most of my program's calls to __aeabi_uldivmod() were with a fixed denominator - this common special-case is often optimized by compilers by replacing division with multiplication by the inverse - since we're dealing with integers, they actually use multiplication by a scaled inverse, something like replacing x/N with x * (2^32/N), then shifting the result right to drop off the remainder. Here's what we need to optimize(and some related functions, like ns_to_us, ns_to_ms, which can be done similarly):
uint64_t ns_to_s( uint64_t ns64 )
{
return ns64 / 1000000000ULL;
}
And it turns out GCC does know this trick, at least aarch64 GCC10.2.1 does. When we compile this we get:
mov x1, 23123 #Load part of a contant into x1
lsr x0, x0, 9 #x0 is ns64, shift it right 9 bits(divide by 512)
movk x1, 0xa09b, lsl 16 #load more bits into x1
movk x1, 0xb82f, lsl 32 #...
movk x1, 0x44, lsl 48 #...
umulh x0, x0, x1 #multiply x0 by x1, keeping only upper 64 bits(discarding 64lsbs)
lsr x0, x0, 11 #unsigned shift right 11 more bits(
ret
But when we compile with 32-bit arm GCC10.2.1, we get a call to uldivmod.
ns_to_s:
@ args = 0, pretend = 0, frame = 0
@ frame_needed = 0, uses_anonymous_args = 0
push {r3, lr}
adr r3, .L14
ldrd r2, [r3]
bl __aeabi_uldivmod(PLT)
pop {r3, pc}
.L14:
.word 1000000000
.word 0
At first I thought this made sense, since 32-bit arm doesn't have a umulh instruction that takes two 64bit registers and multiplies them together to compute a 128bit result then truncates it. But 32bit by 32bit multiplication with 64bit result is relatively quick on 32-bit arm cores, and add and subtract instructions can be chained together to do a 128-bit add in only 4 instructions. If only I had a umulh function, the aarch64 division trick above could be made to work...
The hack
...why not implement one?
At first I started with a slightly naive approach to 128-bit addition by adding after each multiplication using a uint64_t. However, these additions can be overlapped - several uint32_ts can be added together with a uint64_t result without overflowing. By pipelining the 128-bit accumulator to operate LSBs to MSBs, 32 bits at a time, several instructions can be optimized out, and since 64 LSBs are dropped in the result, only their carry-bits are needed. Here's what I came up with:
uint64_t umulh( uint64_t a, uint64_t b )
{
const uint32_t a_lo = a;
const uint32_t a_hi = a >> 32;
const uint32_t b_lo = b;
const uint32_t b_hi = b >> 32;
/* FOIL method of multiplication
See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FOIL_method,
but instead of binomials with constants a,b,c,d variables x,y: (ax+b) * (cy + d),
consider it with variables a,b,c,d, constants x,y = 1<<32 */
const uint64_t acc0 = (uint64_t)a_lo * b_lo;
const uint64_t acc1 = (uint64_t)a_hi * b_lo;
const uint64_t acc2 = (uint64_t)a_lo * b_hi;
const uint64_t acc3 = (uint64_t)a_hi * b_hi;
/* Break up into 32-bit values */
const uint32_t lo0 = acc0;
const uint32_t hi0 = acc0 >> 32;
const uint32_t lo1 = acc1;
const uint32_t hi1 = acc1 >> 32;
const uint32_t lo2 = acc2;
const uint32_t hi2 = acc2 >> 32;
const uint32_t lo3 = acc3;
const uint32_t hi3 = acc3 >> 32;
/* The first 32 bits aren't used in the result,
no need to store them, so no need to compute them.
In fact, don't even worry about res0, start computing res1*/
uint64_t acc = 0;
const uint32_t res0 = lo0;
acc += hi0;
acc += lo1;
acc += lo2;
const uint32_t res1 = acc;
acc >>= 32;
acc += hi1;
acc += hi2;
acc += lo3;
const uint32_t res2 = (uint32_t)acc;
acc >>= 32;
acc += hi3;
const uint32_t res3 = (uint32_t)acc;
return (((uint64_t)res3) << 32 ) + res2;
}
uint64_t ns_to_s_inv( uint64_t ns64 )
{
//constants and shifts from aarch-64 GCC
return umulh( 0x44b82fa09b5A53ULL, ns64 >> 9 ) >> 11;
}
Results
I timed it on an nRF52, and it beats all __aeabi_uldivmod implementations I've seen so far, though udiv based approachs are quite close.
| Algorithm\InstructionCache | Disabled | Enabled |
|---|---|---|
| ns_to_s()/__aeabi_uldivmod - traditional | 50.4-64us | 30.8-40.8us |
| ns_to_s()/__aeabi_uldivmod - udiv based | 2.64-3.36us | 2.16-4.64us |
| ns_to_s_inv()/umulh | 1.26us | 1.09us |
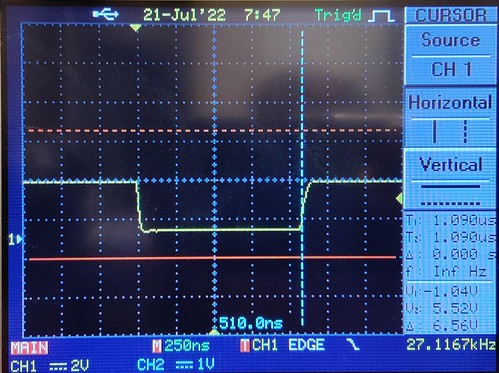
This comes roughly to a 25x to 50x runtime improvement from where I started. The reason for some of this variability is that __aeabi_uldivmod() often takes a different number of cycles based on the values of the inputs. When I saw this in the timing with my oscilloscope, I set the oscilloscope to trigger on the start of each computation, then average 256x resulting triggers together.
Oscilloscope captures
__aeabi_uldivmod common approach: 30.8-40.8 microseconds depending on numerator, or around 2300 machine cycles.
Now here's GCC11 for Cortex-M3/M4's udiv-based approach: 2.16-4.64 microseconds depending on numerator, or around 220 machine cycles. Note the below plot is zoomed in 5x from the above plot.
And here's my umulh-emulation-based approach - averaging is still on, but since the umulh-based approach contains no loops or other data-dependent control-flow the calculation time is far more repeatable when given different inputs, always taking 1.09 microseconds or 70 machine cycles. Also note this is 20x zoomed in time compared to the first plot:
Applicability
Generally, the umulh-based approach above may apply to any machine with a 32 bit x 32 bit multiply instruction with 64-bit result. This instruction is called umull for ARM cores. When a 32-bit udiv instruction is available, __aeabi_uldivmod is competitive on: Cortex-M3, M4, M33, M35P, M55, and newer Cortex-A cores including Cortex-A7, Cortex-A15, Cortex-A53, Cortex-A57. Cores with umull but without udiv is where the umulh approach really shines: ARM7TDMI, ARM9, ARM10, ARM11, Cortex-A8, and Cortex-A9. Possibly also XScale and StrongARM.